How to Decrypt BeFirst Ransomware (.befirst1) and restore data?
Our BeFirst Decryptor: Expert-Built and Enterprise-Tested
BeFirst ransomware is one of the latest variants of the notorious MedusaLocker family, using advanced encryption and double extortion techniques to hold corporate and individual data hostage. Our cybersecurity research team has reverse-engineered several BeFirst samples and developed a specialized decryptor compatible with Windows-based infrastructures.
Built through months of cryptographic analysis, the BeFirst Decryptor combines AI-based file mapping and cloud-integrated integrity checks to ensure safe data restoration without altering the original files. It’s engineered for accuracy, reliability, and speed, with compatibility across on-premise and hybrid environments.
Related article: How to Remove .3e1f9bae9f ransomware and Restore Encrypted Files?
How Our Decryptor Works?
- AI & Blockchain Validation – Encrypted files are scanned through a secure cloud system that uses blockchain technology to verify decryption authenticity and prevent data corruption.
- Victim ID Mapping – Each ransom note includes a unique personal ID, allowing our decryptor to match the exact encryption set.
- Universal Decryption Module – For victims missing the ransom note, a universal mode can handle multiple BeFirst variants by analyzing their cryptographic headers.
- Read-Only Assessment – Before decryption, the tool performs a read-only scan to determine file recoverability and encryption integrity.
Also read: How to Remove WhiteLock Ransomware (.whitelock) and Recover Data?
Immediate Response After a BeFirst Ransomware Attack
Once BeFirst infiltrates a system, it rapidly encrypts files and appends the “.befirst1” extension. The first few minutes are critical — every action counts toward recovery success.
1. Isolate the Infected Systems
Disconnect affected systems immediately from the network to stop the ransomware from spreading to mapped drives, shared folders, or backup servers.
2. Preserve All Artifacts
Do not delete ransom notes (“READ_NOTE.html”) or encrypted files. Preserve system logs, memory dumps, and network activity reports for forensic analysis.
3. Avoid Rebooting or Modifying Files
Restarting infected systems can trigger secondary encryption scripts or wipe memory-stored decryption keys. Avoid renaming, moving, or editing any encrypted file.
4. Contact Professional Recovery Teams
Do not attempt random decryptors found online. Most contain hidden malware or incorrect algorithms that cause permanent data loss. Reach out to verified cybersecurity experts to initiate a structured recovery plan.
Free BeFirst Ransomware Recovery Options
1. Backup Restoration
If offline or cloud backups were maintained, restoring from a clean snapshot remains the most effective solution. Verify the integrity of each backup using checksum validation before initiating recovery to avoid reinfecting restored environments.
2. Shadow Copy Recovery
Although BeFirst typically deletes shadow copies, victims may occasionally find unaltered restore points on external or networked systems. Using shadowexplorer can reveal recoverable files if deletion was incomplete.
Paid Recovery Options: Secure and Verified Methods
1. Negotiated Decryption (Not Recommended)
Some organizations may choose to negotiate with attackers for a decryptor, though this approach carries enormous risk. Many victims report receiving non-functional or incomplete tools after payment. Furthermore, ransom payments may violate legal regulations and encourage continued cybercrime.
2. Third-Party Recovery Experts
Professional negotiators and forensic analysts can serve as intermediaries between victims and ransomware operators. Their role includes validating decryption proof, reducing ransom amounts, and confirming legitimacy of provided tools. However, fees are high, often based on a percentage of the demanded ransom.
3. Our Specialized BeFirst Decryptor
Our proprietary BeFirst Decryptor offers a legitimate, tested alternative to ransom payment. Developed after extensive research into the MedusaLocker family’s cryptography, it leverages unique login ID matching and AI-driven blockchain analysis for secure decryption.
All decryption takes place within sandboxed cloud environments, ensuring that file restoration is verifiable, traceable, and safe from reinfection. Victims simply submit encrypted samples and ransom notes for analysis, after which a recovery plan and timeline are provided.
Step-by-Step BeFirst Recovery Process with BeFirst Decryptor
Assess the Infection
Begin by identifying all encrypted files across the system. BeFirst typically renames files with extensions like .befirst1, .befirst2, or similar variants. Confirm the presence of the ransom note file named READ_NOTE.html, as it contains your unique Victim ID and other communication details.
Secure the Environment
Immediately disconnect the compromised devices from all local and network connections. This prevents the ransomware from propagating to shared storage or backup drives. Ensure that all active encryption scripts are terminated before attempting any recovery actions.
Engage Our Recovery Specialists
Contact our ransomware recovery team and submit a few encrypted sample files along with the ransom note. Our analysts will identify the exact BeFirst variant affecting your system and provide an estimated recovery timeline based on encryption complexity and system architecture.
Run the BeFirst Decryptor
Once variant analysis is complete, download and launch the BeFirst Decryptor with administrator privileges to ensure full functionality. A stable internet connection is required for the decryptor to securely communicate with our cloud servers and validation framework.
Enter Your Victim ID:
Locate the Victim ID within the “READ_NOTE.html” ransom note and enter it into the decryptor. This ensures that your files are mapped accurately to the correct encryption pattern.
Start the Decryptor:
After configuration, initiate the decryption process. The tool will automatically restore your encrypted files to their original state while maintaining their data integrity and structure.
Also read: How to Decrypt Crypz Ransomware (.crypz) files safely?
Offline vs Online Decryption Methods
Offline Decryption:
Ideal for high-security or air-gapped environments, the offline mode allows you to perform recovery without a live internet connection. You only need to transfer encrypted files via secure external media to a clean, isolated recovery system.
Online Decryption:
For faster and fully managed recovery, online decryption connects directly to our secure blockchain-based servers. This mode enables live monitoring, expert assistance, and continuous verification throughout the decryption process.
The BeFirst Decryptor supports both modes, offering flexible recovery solutions for enterprise, government, and industrial networks, ensuring minimal downtime and maximum data safety.
BeFirst Ransomware: Technical Overview
BeFirst ransomware functions through a hybrid encryption process that combines AES and RSA algorithms. After infecting the host, it encrypts accessible data and renames files by appending the “.befirst1” extension (the number may vary, e.g., .befirst2 or .befirst3).
The ransomware then changes the desktop wallpaper and drops an HTML ransom note titled “READ_NOTE.html”, instructing victims to contact the attackers within 72 hours via Tor or encrypted email channels.
If the deadline passes, the ransom demand increases, and attackers threaten to leak exfiltrated data to the public or sell it on dark web forums.
Ransom Note Analysis
BeFirst’s ransom note resembles that of other MedusaLocker variants. It assures victims that their files are “safe, only modified (RSA+AES)” and warns against using third-party tools. Victims are told to send two or three non-critical files for free decryption as proof of legitimacy.
Your personal ID:
–YOUR COMPANY NETWORK HAS BEEN PENETRATED
Your files are safe! Only modified.(RSA+AES)
ANY ATTEMPT TO RESTORE YOUR FILES WITH THIRD-PARTY SOFTWARE WILL PERMANENTLY CORRUPT IT. DO NOT MODIFY ENCRYPTED FILES. DO NOT RENAME ENCRYPTED FILES.
No software available on internet can help you. We are the only ones able to solve your problem. We gathered highly confidential/personal data. These data are currently stored on a private server. This server will be immediately destroyed after your payment. If you decide to not pay, we will release your data to public or re-seller. So you can expect your data to be publicly available in the near future.. We only seek money and our goal is not to damage your reputation or prevent your business from running. You will can send us 2-3 non-important files and we will decrypt it for free to prove we are able to give your files back.
Contact us for price and get decryption software.
email:
support1@bancerc.com
support2@norviscon.com* To contact us, create a new free email account on the site: protonmail.com
IF YOU DON’T CONTACT US WITHIN 72 HOURS, PRICE WILL BE HIGHER.
* Tor-chat to always be in touch:
Behavioral Indicators and Encryption Pattern
BeFirst targets all major file types — including documents, images, archives, and databases. It modifies file headers during encryption, ensuring standard recovery tools fail to recognize them.
It avoids encrypting system-critical directories to keep the OS bootable. The ransomware also deletes Windows shadow copies, eliminating quick restore options. After encryption, it deploys registry entries to maintain persistence.
Attack Vectors and Initial Access Techniques
BeFirst ransomware infiltrates systems through multiple channels, often exploiting human error and unpatched vulnerabilities. Common entry points include:
- Phishing emails with malicious attachments (often disguised as invoices or shipping documents).
- Infected archive files (ZIP, RAR) that unpack executable payloads.
- Malvertising campaigns distributing drive-by downloads.
- Compromised remote desktop services (RDP) with weak or reused passwords.
- Software cracks and fake update installers found on torrent or warez sites.
Once executed, BeFirst connects to a remote command-and-control (C2) server to exchange encryption keys and begin its payload execution.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
BeFirst aligns with several techniques defined in the MITRE ATT&CK framework:
| MITRE Tactic | Technique | Description |
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Phishing via email attachments and links |
| Execution | T1204 | User execution of malicious file |
| Persistence | T1547 | Modifies registry keys for startup persistence |
| Defense Evasion | T1562 | Disables antivirus and deletes shadow copies |
| Credential Access | T1003 | Attempts credential theft for lateral movement |
| Exfiltration | T1048 | Uploads data over encrypted channels before encryption |
| Impact | T1486 | Encrypts files using AES+RSA |
Tools Used and Operational Artifacts
BeFirst operators use a combination of legitimate administrative and malicious tools to evade detection and sustain persistence:
- Mimikatz – Extracts saved credentials from memory.
- PsExec – Enables remote code execution across networks.
- 7-Zip and WinRAR – Compress stolen data for exfiltration.
- AnyDesk / RAdmin – Remote access tools for continued control.
- vssadmin & wbadmin – Used to delete shadow copies and backups.
- PowerShell scripts – Execute encryption payloads and network scans.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
File Extensions: .befirst1, .befirst2, etc.
Ransom Note: READ_NOTE.html
Contact Emails: support1@bancerc.com, support2@norviscon.com
Registry Modifications: Startup entries under HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Dropped Files: BeFirst.exe, temporary payloads under %AppData%
Network Behavior: Outbound connections to Tor nodes and unknown IPs.
These indicators can be cross-referenced with system logs to confirm an infection event.
BeFirst Victim Analysis and Data Trends
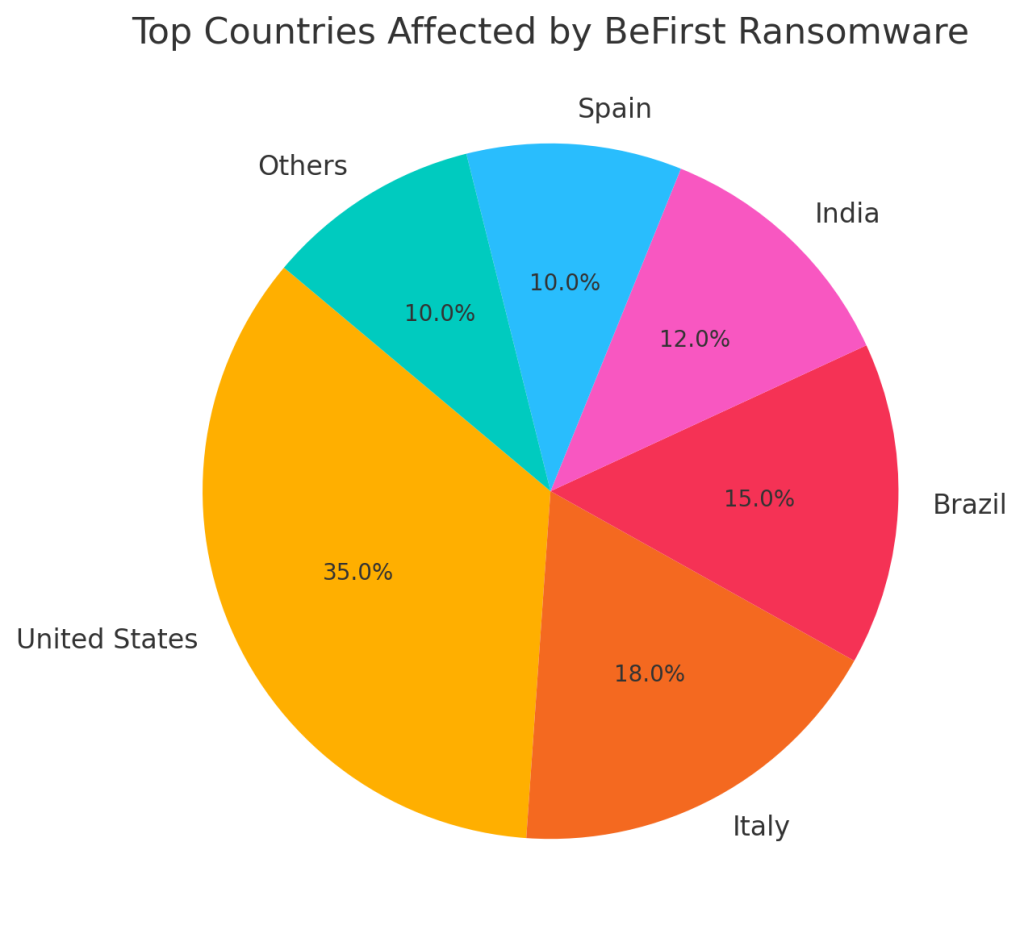
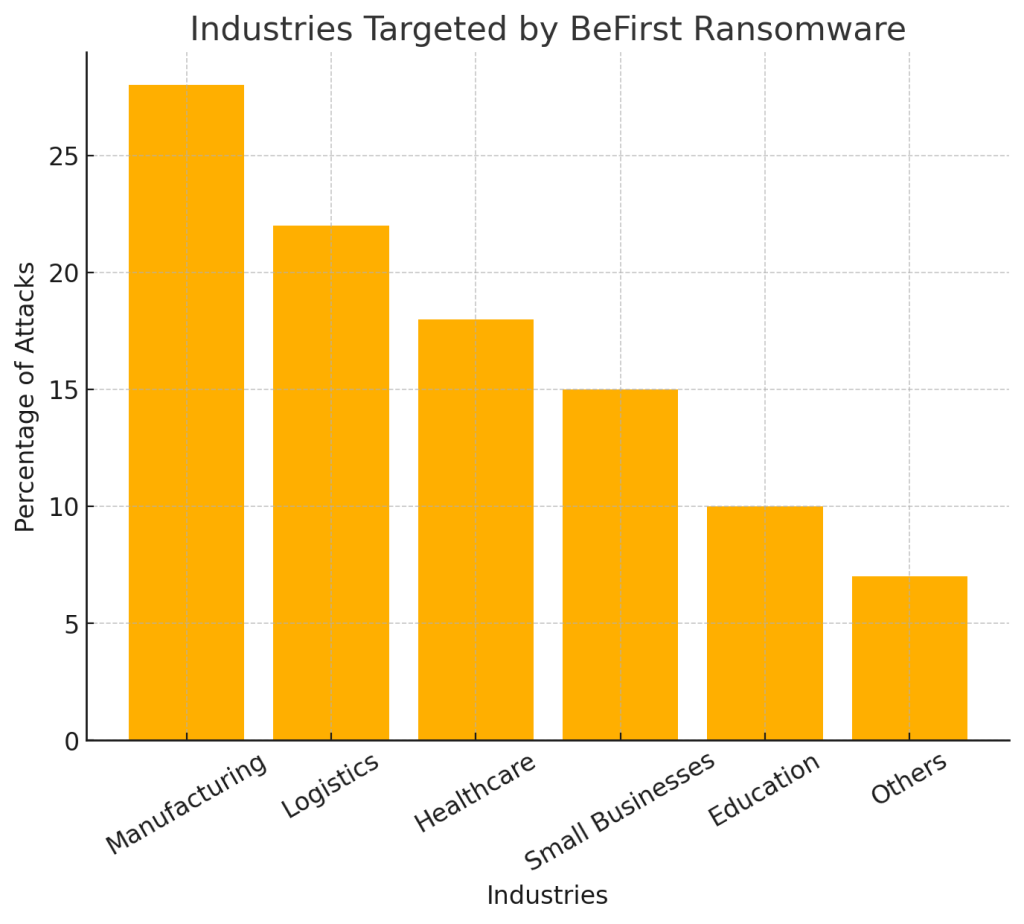
BeFirst has primarily targeted corporate environments across manufacturing, healthcare, education, and government sectors. Most campaigns observed so far have focused on North America and Europe, with sporadic incidents in Asia.
Target countries
Target Sectors
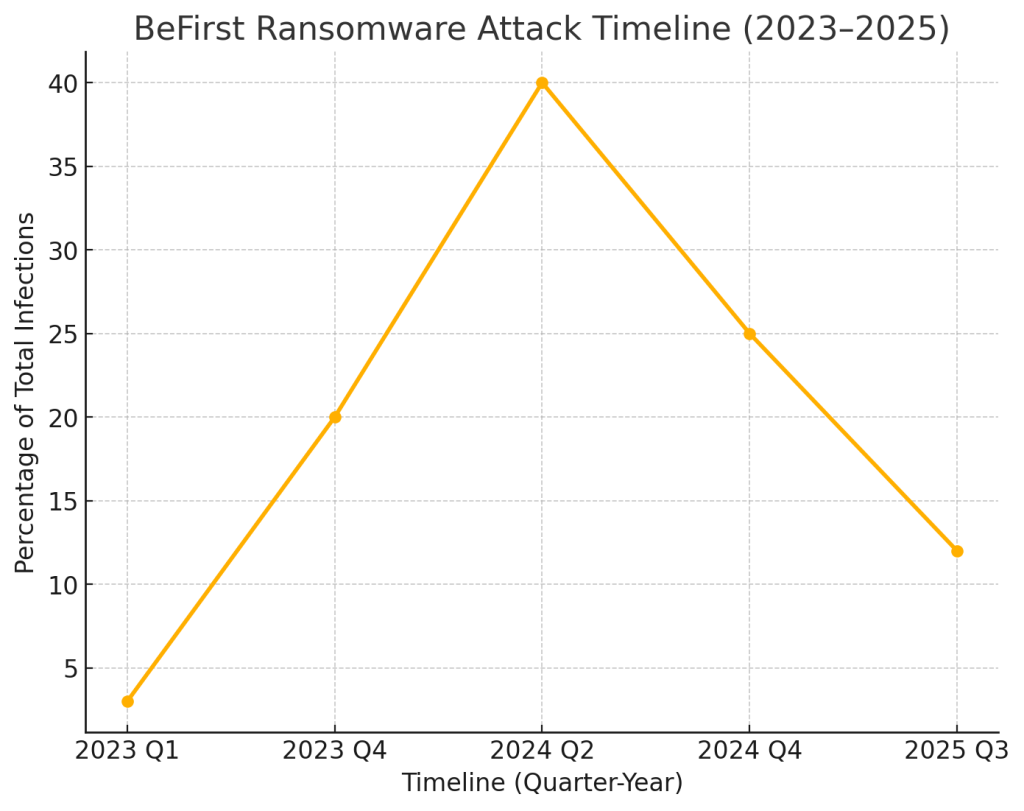
Attack Timeline
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Maintaining security hygiene can significantly reduce ransomware risk:
- Use multi-factor authentication for RDP and VPN access.
- Regularly patch operating systems and firmware.
- Maintain immutable and offline backups.
- Employ a reliable EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) solution.
- Train employees to identify phishing attempts.
Conclusion: Recover, Restore, and Reinforce
BeFirst ransomware’s encryption and extortion tactics may appear insurmountable, but with swift action and expert-led recovery, full restoration is possible. Victims should avoid panic-driven decisions and rely on verified recovery solutions such as our BeFirst Decryptor, which provides safe, traceable, and effective restoration without paying criminals.
Whether your organization is facing an enterprise-wide encryption event or a localized breach, acting fast, preserving evidence, and contacting professionals can make all the difference between total loss and full recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Contact Us To Purchase The BeFirst Decryptor Tool






